简介
迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra) 是由荷兰计算机科学家狄克斯特拉于1959年提出的,因此又叫狄克斯特拉算法。是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有权图中最短路径问题。迪杰斯特拉算法主要特点是从起始点开始,采用贪心算法的策略,每次遍历到始点距离最近且未访问过的顶点的邻接节点,直到扩展到终点为止。
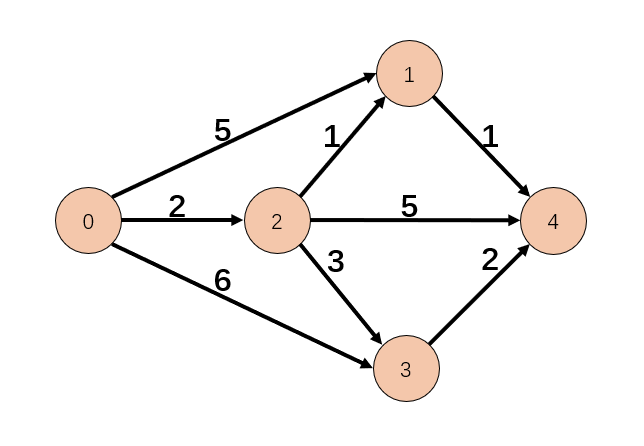
注意,
Dijkstra算法无法处理负权边的情况,比如 0 到 2 点的距离为:-2。
松弛操作(Relaxation)
何为松弛操作,文字描述比较抽象,看图吧。
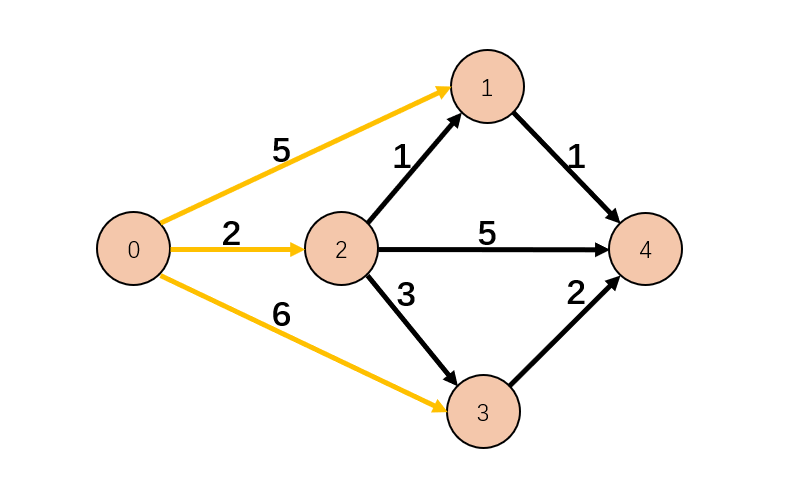
0 的邻点有 1、2、3,距离分别是 5、2、6,这其中,距离最短的是 2,到点 2,那么就可以推断出 0 到 2 的距离肯定是最短的。为什么?假设还有一条边从 1 到 2 的。
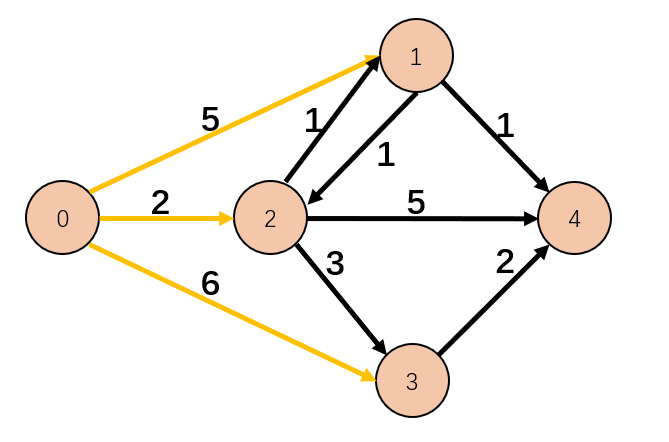
路径 0 - 1 的距离是 5,就光这一条边的距离已经超过了 0 - 2 的距离 2 了,再从 1 连接到 2,距离是 1,那总距离是 6,肯定没有 0 - 2 的距离短。那 0 - 3 - 2 就更不用说了,0 - 3 的距离已经是 6 了。
注意:以上都是不存在负权边的情况,假设 1 - 2 的距离是 -4,那就不一样了。Dijkstra 不能处理负权边。
松弛操作
上边已经找到 0 - 2 是第一次查找的最短路径,开始以 2 为基础进行松弛操作。
遍历点 2 的邻点,查看以点 2 为基础距离(现在到点 2 的基础距离为 2),再加上点 2 到其邻点的距离,是否比原来已知的能到达邻点的距离短。如下图:
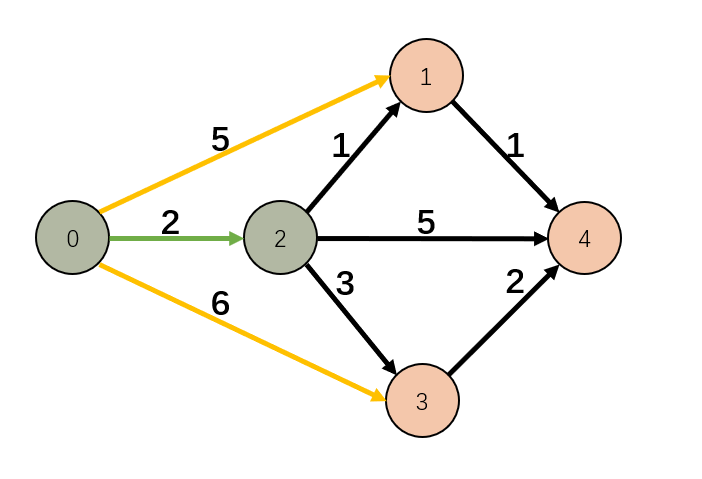
- 2 - 1 的距离为 1,再加上点 2 的基础距离 2,得出 0 - 2 - 1 的总距离为:3。
- 原到点 1 的距离是 0 - 1 的距离 5,显然此次松弛操作后,0 - 2 - 1 的距离是更短的,把到点 1 的距离更新为:3。
- 2 - 3 的距离为 3,再加上点 2 的基础距离 2,得出 0 - 2 - 3 的总距离为:5。
- 原到点 3 的距离是 0 - 1 的距离 6,显然此次松弛操作后,0 - 2 - 3 的距离是更短的,把到点 1 的距离更新为:5。
- ......
总结来说就是找到一个已经确定了为最短路径的点,这里就是点 2,以其为基础距离,看其到邻点的距离是否更优。更优则更新,否则跳过。
实现
0 到其他点的最短距离动画演示
先以 0 为起点到其他所有点的最短距离观察一下。

代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include "../help/Edge.h"
#include "IndexMinHeap.h"
/**
* Dijkstra 算法求最短路径
*
* 时间复杂度:O(Elog(V))
*/
template<typename Graph, typename Weight>
class Dijkstra {
private:
/**
* 图
*/
Graph &G;
/**
* 起始点
*/
int s;
/**
* 存放已探索到的点,从 s 到这些点的距离
*/
Weight *distTo;
/**
* 点是否已经找到了最短路径
*/
bool *marked;
/**
* 记录当前点是从那个点过来的
* 通过此字段可以反推 s 到任一点的最短路径
*/
vector<Edge<Weight> *> from;
/**
* 在松弛过后用来获取已探索路径中最短的点
*/
IndexMinHeap<Weight> ipq;
public:
Dijkstra(Graph &graph, int s) : G(graph), ipq(IndexMinHeap<Weight>(graph.v())) {
assert( s >= 0 && s < G.v() );
// 初始化成员变量
this->s = s;
distTo = new Weight[G.v()];
marked = new bool[G.v()];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.v(); ++i) {
distTo[i] = Weight();
marked[i] = false;
from.push_back(nullptr);
}
// 因为从 s 点开始,s 点的就可以固定初始化一下
// 到 s 点的上一个点也是 s 自己。
from[s] = new Edge<Weight>(s, s, Weight());
// 把 s 放入已探索最小索引堆,等待取出
ipq.insert(s, Weight());
while (!ipq.isEmpty()) {
Weight v = ipq.extractMinIndex();
// 新取出的已探索最短距离点必然是最短路径
marked[v] = true;
// 遍历 v 的邻边进行松弛操作。
typename Graph::AdjIterator adjIter(G, v);
for (Edge<Weight> *e = adjIter.begin(); !adjIter.end(); e = adjIter.next()) {
// 获取当前这条边与 v 相连的点
int w = e->other(v);
// 点 w 没有被标记过"已经找到最短历经"的情况下再继续
if (!marked[w]) {
// 如果点 w 没有被探索过 || 已经被探索过,但是新的路径距离更短
if (nullptr == from[w] || distTo[v] + e->wt() < distTo[w]) {
from[w] = e;
distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e->wt();
if (ipq.contain(w)) {
// 更新索引堆中的路径距离
ipq.change(w, distTo[w]);
} else {
// 新增
ipq.insert(w, distTo[w]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
~Dijkstra() {
delete[] distTo;
delete[] marked;
delete from[s];
}
/**
* 返回从 s 点到 w 点的最短路径长度
*/
Weight shortestPathTo(int w) {
assert(w >= 0 && w < G.v());
assert(hasPathTo(w));
return distTo[w];
}
/**
* 判断从 s 点到 w 点是否联通
*/
bool hasPathTo(int w) {
assert(w >= 0 && w < G.v());
return marked[w];
}
/**
* 寻找从 s 到 w 的最短路径, 将整个路径经过的边存放在 vec 中
*/
void shortestPath(int w, vector<Edge<Weight>> &vec) {
assert(w >= 0 && w < G.v());
assert(hasPathTo(w));
// 通过from数组逆向查找到从s到w的路径, 存放到栈中
stack<Edge<Weight> *> s;
Edge<Weight> *e = from[w];
while (e->v() != this->s) {
s.push(e);
e = from[e->v()];
}
s.push(e);
// 从栈中依次取出元素, 获得顺序的从s到w的路径
while (!s.empty()) {
e = s.top();
vec.push_back(*e);
s.pop();
}
}
/**
* 打印出从 s 点到 w 点的路径
*/
void showPath(int w) {
assert(w >= 0 && w < G.v());
assert(hasPathTo(w));
vector<Edge<Weight>> vec;
shortestPath(w, vec);
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) {
cout << vec[i].v() << " -> ";
if (i == vec.size() - 1)
cout << vec[i].w() << endl;
}
}
};测试
// testG1.txt
5 8
0 1 5
0 2 2
0 3 6
1 4 1
2 1 1
2 4 5
2 3 3
3 4 2void testDijkstra() {
string filename = "testG1.txt";
int v = 5;
SparseGraph<int> g = SparseGraph<int>(v, true);
// Dijkstra最短路径算法同样适用于有向图
// SparseGraph<int> g = SparseGraph<int>(v, false);
ReadGraph<SparseGraph<int>, int> readGraph(g, filename);
cout << "Test Dijkstra:" << endl << endl;
Dijkstra<SparseGraph<int>, int> dij(g, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
if (dij.hasPathTo(i)) {
cout << "Shortest Path to " << i << " : " << dij.shortestPathTo(i) << endl;
dij.showPath(i);
} else
cout << "No Path to " << i << endl;
cout << "----------" << endl;
}
}show:
Test Dijkstra:
Shortest Path to 0 : 0
0 -> 0
----------
Shortest Path to 1 : 3
0 -> 2 -> 1
----------
Shortest Path to 2 : 2
0 -> 2
----------
Shortest Path to 3 : 5
0 -> 2 -> 3
----------
Shortest Path to 4 : 4
0 -> 2 -> 1 -> 4
----------
文章评论